Osteochondrosis is a disease caused by degenerative-dystrophin changes in vertebrae, intervertebral discs and ligaments. People after 30 years are the most sensitive to the disease, but the initial manifestations of the disease may occur in adolescence.
80-90% of the population faces this disease.
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the location of the pathological focus, there are 3 forms of diseases differ:
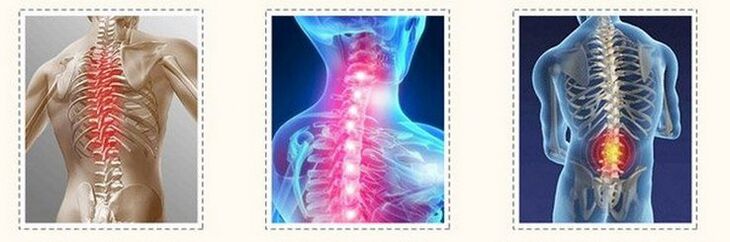
- Osteochondrosis of cervical regions
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
- Osteochondrose of the lumbar region
With damage to the cervix the mother spine, the patient's complaints are related to insufficient brain nutrition due to splashing blood vessels. The most common appeal is a strong headache and dizziness. In addition, patients are concerned:
- Board of blood pressure
- Disorders of the coordination of movement and shake of walking
- Vision sharpness reduction;
- Hearing aggravation, ringing in ears
- Hoarse or hoarse
- Snoring in a dream is a permanent tension of the neck muscles.
When compressing nerves, stiffness and cooling fingers, weakness in the limbs in the limbs.
If the nerves are sent, heavy neck pain, pain in the scalp, sore throat, teeth. The pain extends to shoulders and limb.
The symptom of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is also pain - intercostal neuralgia. Pain is due to compression of nerve roots. The pain in the chest is acute, is intensified by coughing, inspiration, laughter, when moving.
The pain for osteochondrose of the thoracic region can simulate other diseases, for example, heartache, abdominal pain.
Lumbar osteohondrose usually affects people who have a seated job. It is characterized by the pain in the lower back that are given buttocks and legs. With violations of nerves, stiffness and cooling legs, the possibility of sensitivity, feces and urine incontinence are possible.
The causes of the disease
The disease is considered polyethological, ie many factors contribute to the disease. Most often:
- A strong day load on the spine
- Spine injuries
- Metabolic disorders
- Overweight
- Curvature of the spinal column
- Hereditary factor
- The process of natural aging of the body.
Diagnostics
Osteochondrose diagnosis consists of several phases.
A collection of anamnesis of disease and life
The doctor asks patient questions to find out:
- Appeal
- Localization of pain and discomfort
- When the first symptoms appeared
- Which causes appearance and increased pain.
- Which helps mitigate the condition.
It is important to find out the working conditions of patients, bad habits than it was ill throughout life, whether there are bruises and spine injuries, whether one of the closest relatives of osteochondrosis.
Inspection and palpation
At the examination, the doctor draws attention to the position of the body and holding, on the symmet of the back and neck.
X -ray testing
Spine radiography is performed in two hair screenings, in direct and lateral for greater information. Sometimes ray research is needed with a functional slope of samples, flexion, expansion position.
Computer Tomography
The CT is a study that allows you to consider the bodies of vertebrae, ligaments, blood vessels and soft tissues more clearly. The image of one or more segments of the spine is performed. CT allows you to determine the compression of nerves, tears and hernia of interfoodbral disks, their height, changes in the solid membrane of the brain, vertebralism.
Magnetic resonant therapy
The MRI is used to diagnose osteochondrose with clear visualization of blood vessels, nerve processes, intersections.
Complications
Osteochondrosis is a disease not only the back, as commonly believed. Determines blood vessels, nerves, muscles. Osteochondrosis causes the development of more related diseases, including:
- Migraine
- Worsening vision and hearing
- Intervertebral hernias
- Schmorm's nodes
- Radiculitis
- Lumbago
- Sciatica
- Spondilas, spondylarthrosis and others.
Treatment treatment
Treat osteochondrose conservatively, in difficult cases - immediately.
Conservative treatment includes the entire complex of therapeutic procedures: massage, physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy, manual therapy, reflexology, spine and medicine.
Medicines are prescribed during aggravation, help alleviate pain, inflammation and normalization of metabolic processes.
Risk group
Osteochondrose risk group includes:
- People who lead a sitting way of life with sitting work or spending a lot of time driving or on a computer
- People whose work or hobby is associated with weight lifting
- People with excess body mass
- Pregnant
- Women who wear high heels.
Prevention
To prevent osteochondrose, it is important to follow the rules:
- Do not overload your spine, limit vertical load
- Filling, strengthen spinal muscles, replace them
- No
- Avoid injuries and bruises spine
- Don't wear weights
- Change body position with long seated load and driving.
Diet and lifestyle
Diet for osteochondrose There is no strict restrictions, can be attributed to proper nutrition. It is necessary to limit salt and sugar. The main thing is that food matches energy costs. If there is a surplus weight, it is necessary to reduce candy consumption and easily absorbed carbohydrates. Replace coffee with tea, sweets - dried fruit.
Each day you have to do exercises, which include: sipping, squats, tilting on the sides, turns the body, running, walking, swinging forward, to the side and back.
Sleeping with osteochondrosis is desirable on a solid surface.
During the long sitting work, you must stretch and turn the body every 20-30 minutes. With a long-term standing, it is important to change to support the point from one leg to another.
If you need to carry weight, you can distribute weight on each hand, you can use a wide belt backpack.
Symptoms
- Headache
- Hoarse voice
- Incontinence urine
- Vague vision
- Wearing
- Shark
- Snore